Why Traditional VPNs Are Failing Modern Enterprise Security
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, traditional perimeter-based security models have become increasingly inadequate. The conventional VPN approach, once the cornerstone of remote access security, now presents significant limitations in an era where cyber threats are more sophisticated and pervasive than ever before.
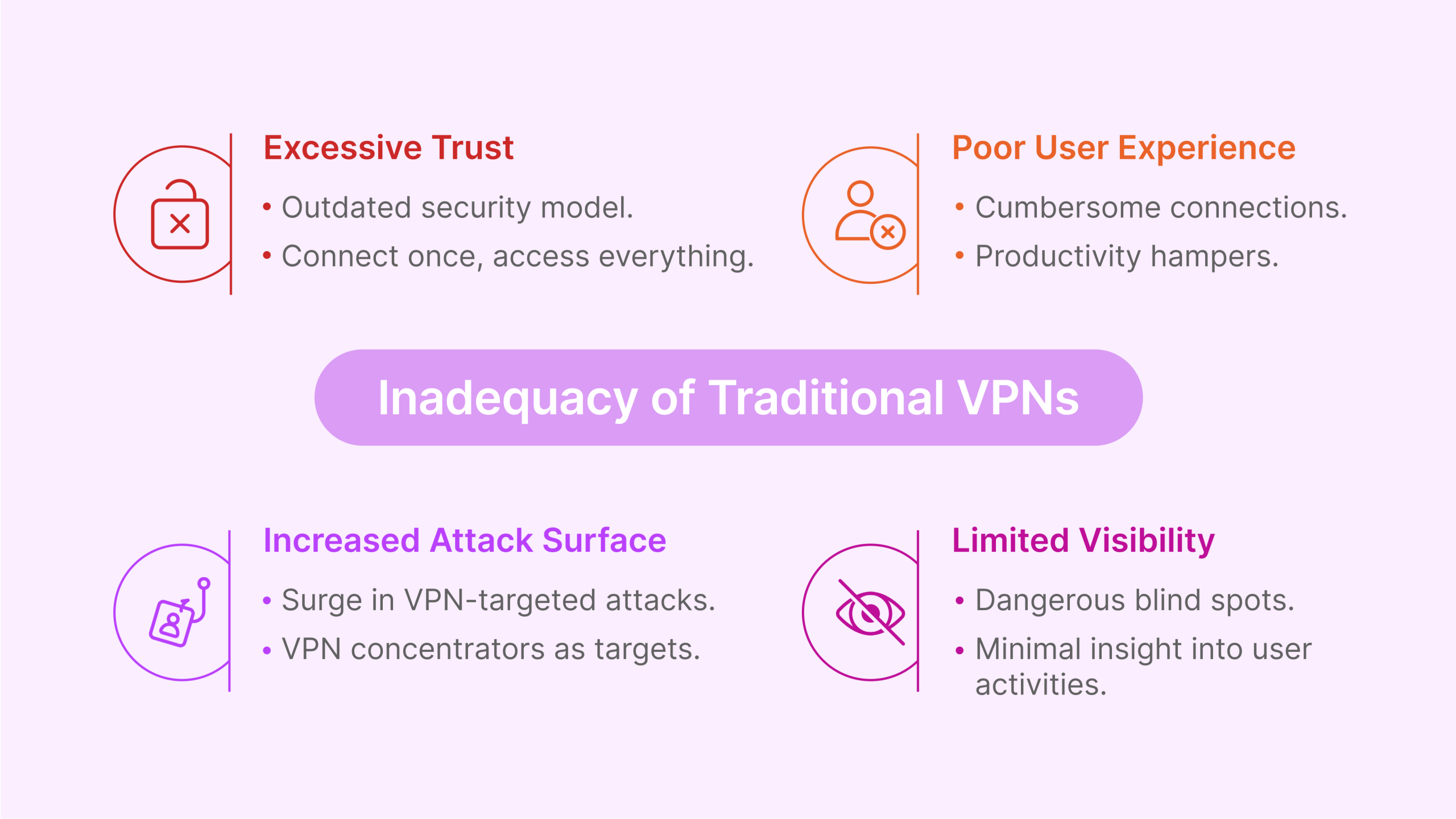
Enterprise security leaders face mounting challenges with traditional VPNs, including:
- Excessive Trust: VPNs operate on an outdated “connect once, access everything” model that grants excessive network privileges once a user authenticates.
- Limited Visibility: Traditional solutions provide minimal insight into user activities after authentication, creating dangerous blind spots.
- Poor User Experience: The cumbersome nature of VPN connections frustrates users and hampers productivity in hybrid work environments.
- Scalability Constraints: Legacy VPN infrastructure struggles to accommodate the explosive growth in remote work demands.
- Increased Attack Surface: VPN concentrators have become prime targets for sophisticated threat actors, as evidenced by the surge in VPN-targeted attacks since 2020.
According to recent industry research, 76% of security leaders report that traditional VPN solutions cannot meet their current security requirements, with 82% actively seeking more adaptive and granular access control mechanisms. This fundamental shift in security requirements has accelerated the adoption of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) as the preferred approach for modern enterprise security.
ZTNA: The Secure Remote Access Solution for Today’s Hybrid Workforce
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a transformative approach to secure access, fundamentally reimagining how organizations protect their digital assets. Unlike traditional security models that implicitly trust users within the network perimeter, ZTNA operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” creating identity- and context-based logical access boundaries around applications rather than networks.
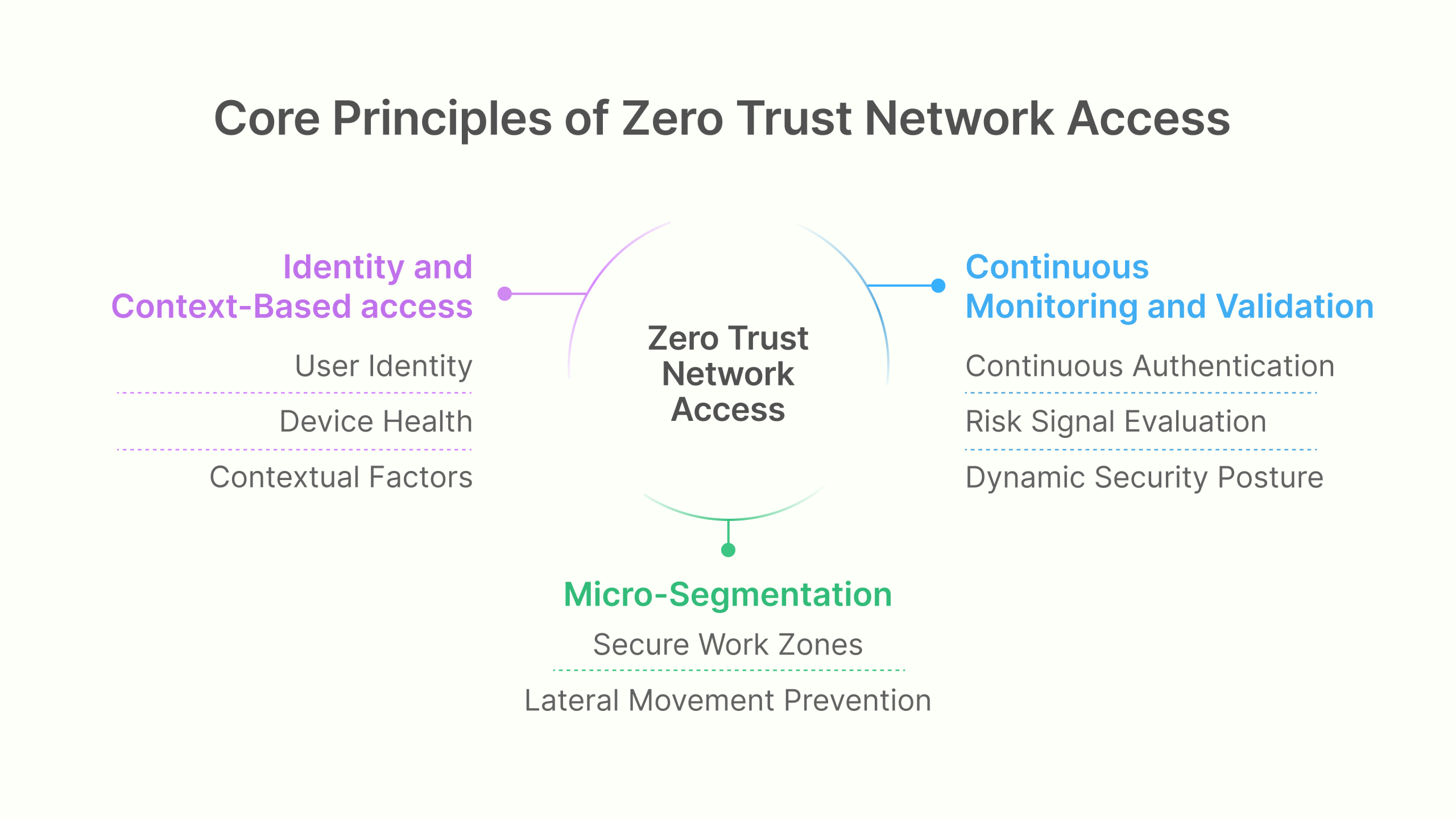
Core principles that define ZTNA
The ZTNA security model is built upon three essential principles that collectively transform the approach to enterprise security:
- Identity and Context-Based Access: ZTNA makes access decisions based on verified user identity, device health, and contextual factors rather than network location. This granular approach ensures that access privileges align precisely with specific requirements, dramatically reducing the risk of lateral movement by threat actors.
- Micro-Segmentation: By breaking the network into smaller, isolated segments, ZTNA creates secure work zones that contain and limit an attacker’s ability to move laterally. This compartmentalization ensures that even if one segment is compromised, the breach remains contained and cannot spread throughout the environment.
- Continuous Monitoring and Validation: ZTNA replaces one-time verification with continuous authentication and authorization. The system constantly evaluates risk signals and can immediately revoke access when suspicious activities are detected, creating a dynamic security posture that adapts to emerging threats in real-time.
The Business Value of ZTNA Implementation
For CISOs and security leaders, ZTNA delivers compelling business advantages that extend far beyond technical security improvements:
- Enhanced Security Posture: By implementing least-privilege access and continuous verification, organizations can reduce their attack surface by up to 70%.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Streamlined access management reduces IT overhead by approximately 40% compared to traditional VPN management.
- Superior User Experience: Contextual, seamless access increases productivity while reducing friction, with 65% of organizations reporting improved user satisfaction after ZTNA implementation.
- Regulatory Compliance: ZTNA’s granular controls and comprehensive logging capabilities simplify compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific requirements.
- Business Agility: The flexible, scalable nature of ZTNA enables organizations to adapt quickly to changing business requirements and support new digital initiatives.
As remote and hybrid work models become permanent fixtures in the enterprise landscape, ZTNA provides the security foundation necessary to support this transformation while maintaining robust protection for critical assets.
Key Components of a Successful ZTNA Implementation Strategy
Implementing Zero Trust Network Access requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses both technical and organizational considerations. Based on insights from successful ZTNA deployments across various industries, the following components are essential for a successful implementation:
Strategic Planning Elements
A well-designed ZTNA strategy must account for current and future security needs while addressing potential implementation challenges:
- Policy Decision Point (PDP) Advancement: By 2027, industry analysts predict that 70% of organizations may experience stalled ZTNA deployments without advancements in policy decision points. Investing in technologies that enhance PDP capabilities is essential for long-term success.
- Asset Management Strategy: Forward-thinking organizations are increasingly excluding unmanaged devices and non-virtualized environments from their initial ZTNA implementations. By 2028, approximately 76% of enterprises will adopt this approach to streamline deployment and reduce complexity.
- Dynamic Access Control Evolution: The most mature ZTNA implementations are moving toward continuous, dynamic, risk-based access controls. By 2027, an estimated 25% of organizations will have fully implemented these advanced capabilities, creating a significant competitive advantage in security posture.
Implementation Roadmap Development
A phased implementation approach maximizes return on investment while minimizing operational disruptions:
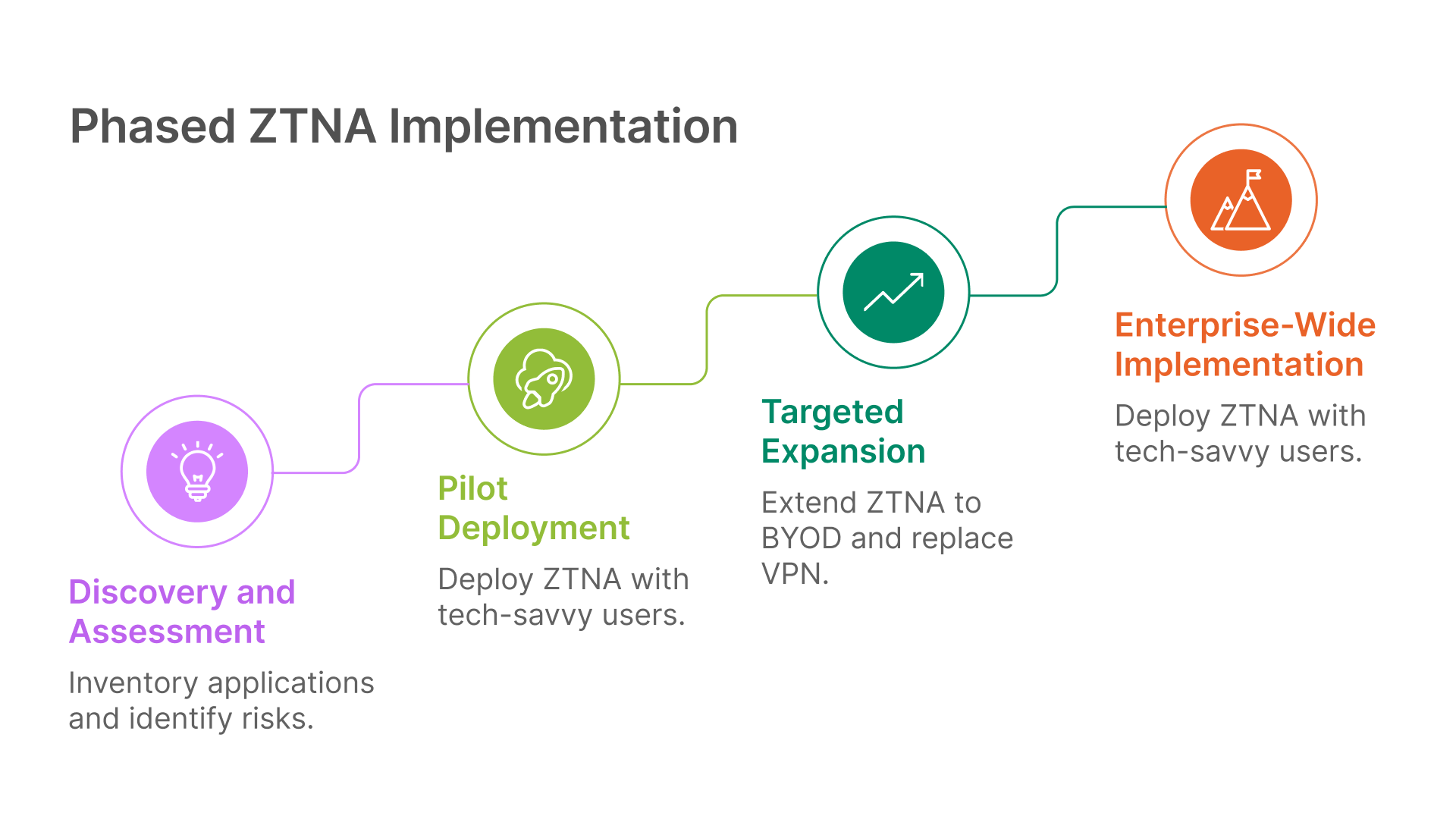
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment
- Inventory all applications and access requirements
- Identify high-risk applications and user groups
- Document current access patterns and security gaps
- Establish baseline metrics for measuring success
Phase 2: Pilot Deployment
- Select technology-savvy users for initial deployment
- Focus on high-risk applications with clear security benefits
- Implement in parallel with existing access methods
- Gather user feedback and performance metrics
Phase 3: Targeted Expansion
- Extend ZTNA to BYOD and extended workforce use cases
- Replace remote access VPN with clientless ZTNA solutions
- Integrate agent-based ZTNA into broader security architecture
- Develop comprehensive training and change management programs
Phase 4: Enterprise-Wide Implementation
- Deploy ZTNA across all user groups and applications
- Integrate with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture
- Implement advanced policy controls and automation
- Establish continuous improvement processes
Organizations that follow this structured approach report 62% faster time-to-value and 45% fewer implementation challenges compared to those attempting comprehensive deployment all at once.
How to Select the Right ZTNA Vendor: Comparison Framework
The ZTNA market has expanded rapidly, with numerous vendors offering solutions that vary significantly in capabilities, architecture, and focus. Selecting the right ZTNA vendor requires a systematic evaluation framework that aligns with your organization’s specific requirements.
Essential Vendor Selection Criteria
When evaluating ZTNA solutions, focus on these critical selection criteria:
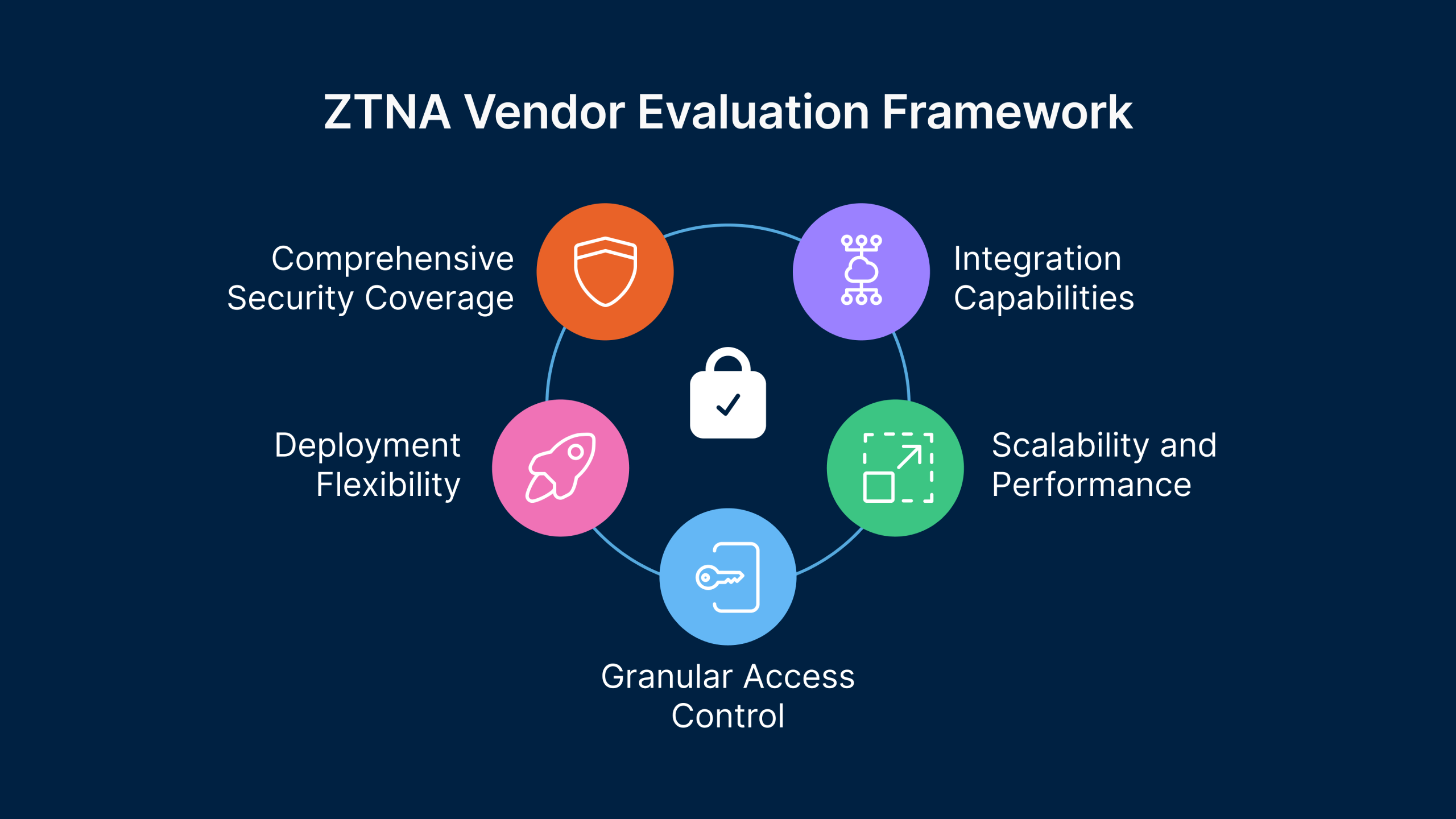
- Comprehensive Security Coverage: The ideal vendor should meet all security requirements for managed devices while offering a clear path to unified, dynamic access control policies. Evaluate how the solution handles various authentication methods, device posture checks, and integration with existing security tools.
- Deployment Flexibility: Choose vendors that support both agent-based and agentless approaches to cover all use cases effectively. This flexibility ensures that your ZTNA solution can accommodate various user scenarios, from corporate-managed devices to BYOD and third-party access.
- Granular Access Control: Implement ZTNA solutions that provide precise, application-level access control for all users and applications. The solution should support attribute-based access control (ABAC) and role-based access control (RBAC) models while enabling policy customization based on your organization’s unique requirements.
- Scalability and Performance: Ensure the trust broker system is redundant to avoid single points of failure and minimize latency issues. The solution should maintain performance under peak loads and scale efficiently as your user base grows.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate how well the ZTNA solution integrates with your existing security ecosystem, including identity providers, endpoint protection platforms, SIEM solutions, and cloud services.
Vendor Comparison Matrix
| Capability | Legacy Providers (Citrix, VMware) | ZTNA-Focused Vendors (Zscaler, Perimeter 81) | Thinfinity Workspace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Model | Primarily on-premises witd cloud options | Cloud-first witd limited on-premises options | Flexible hybrid deployment |
| Agent Requirements | Heavy agent footprint | Lightweight agent witd some agentless options | Agent-optional witd full agentless support |
| Application Support | Limited to web and published apps | Web, SaaS, and some private applications | Comprehensive support for web, legacy, and custom applications |
| Integration Depth | Deep integration witd own ecosystem | Moderate integration witd tdird-party tools | Vendor-neutral witd extensive API support |
| Implementation Complexity | High | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Total Cost of Ownership | High | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| User Experience | Complex | Streamlined for supported apps | Intuitive and consistent across all applications |
This comparison highlights how Thinfinity Workspace delivers a balanced approach that combines the comprehensive application support of legacy solutions with the modern security architecture and user experience of cloud-native ZTNA providers.
Step-by-Step ZTNA Implementation Guide for Enterprise CISOs
Implementing ZTNA effectively requires a structured approach that balances security requirements with operational considerations. This step-by-step guide provides a practical roadmap for CISOs and security leaders to successfully deploy ZTNA in enterprise environments.
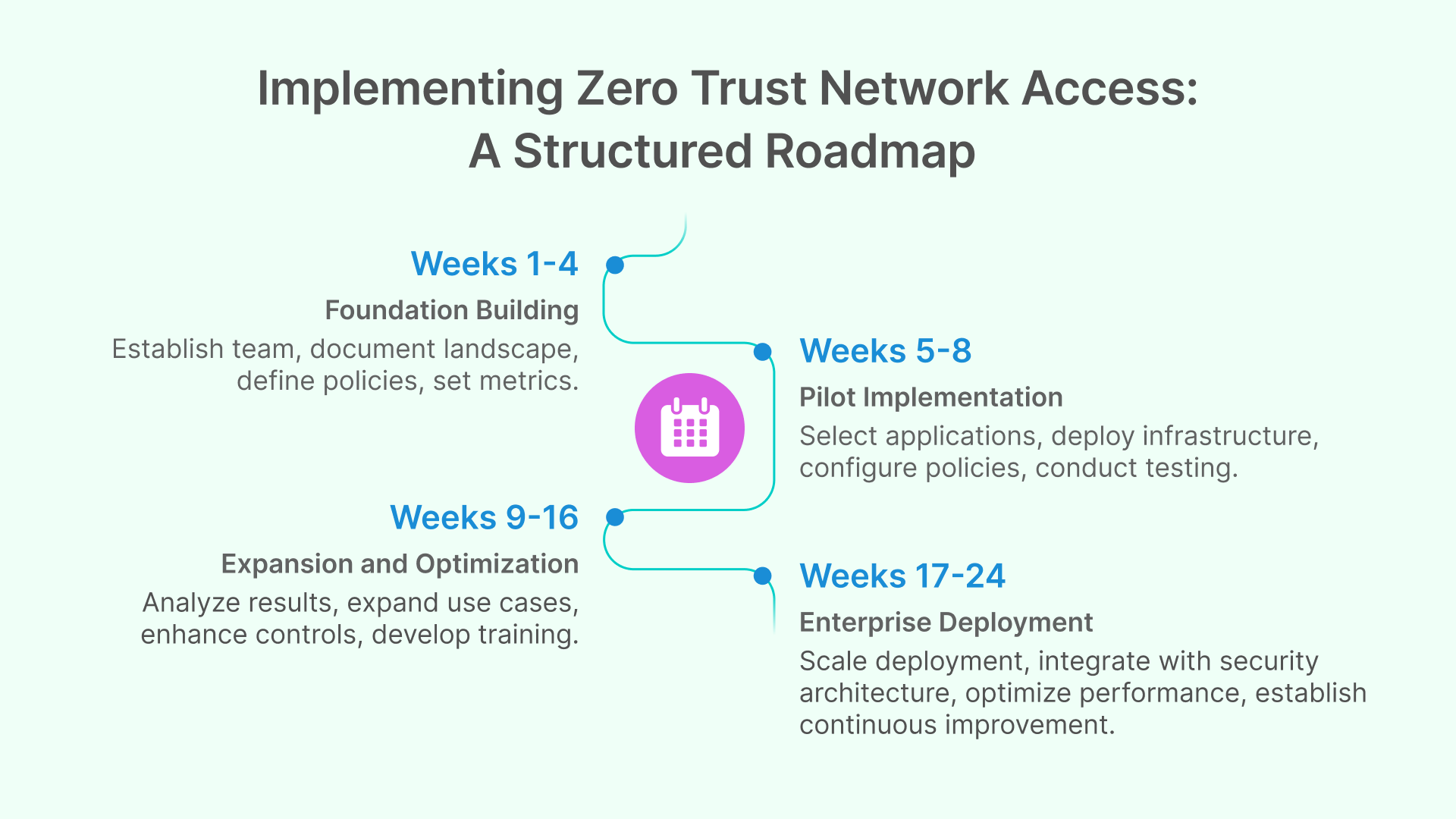
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Weeks 1-4)
1. Establish Your Zero Trust Team:- Identify key stakeholders from security, IT, application owners, and business units
- Define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes
- Secure executive sponsorship and resource commitments
- Inventory all applications requiring remote access
- Classify applications by sensitivity, user base, and business criticality
- Map current access methods and authentication requirements
- Develop least-privilege access policies for each application
- Create user and device classification framework
- Document contextual access requirements (time, location, device posture)
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) for security improvement
- Establish user experience and productivity metrics
- Create baseline measurements for comparison
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Weeks 5-8)
1. Select Pilot Applications and Users:- Identify 2-3 applications for initial deployment
- Select technically proficient users from different departments
- Ensure applications represent different access patterns
- Implement core ZTNA components (controllers, gateways)
- Configure integration with identity providers
- Establish monitoring and logging capabilities
- Implement basic access policies for pilot applications
- Configure device posture checks and authentication methods
- Establish baseline security controls
- Train pilot users on new access methods
- Gather feedback on user experience and performance
- Document and address technical issues
Phase 3: Expansion and Optimization (Weeks 9-16)
1. Analyze Pilot Results:- Review security metrics and user feedback
- Identify areas for policy refinement
- Document lessons learned and best practices
- Deploy ZTNA for BYOD and contractor access
- Implement for high-risk applications
- Begin phased replacement of VPN access
- Implement more granular, context-aware policies
- Configure advanced authentication methods
- Integrate with additional security tools
- Create comprehensive user training materials
- Develop administrator documentation
- Establish support processes and escalation procedures
Phase 4: Enterprise Deployment (Weeks 17-24)
1. Scale Deployment Enterprise-Wide:- Roll out ZTNA access to all user groups
- Migrate remaining applications from legacy access methods
- Implement in parallel with existing solutions before cutover
- Connect ZTNA with SIEM and security analytics
- Implement automated response workflows
- Integrate with cloud security and CASB solutions
- Fine-tune policies based on usage patterns
- Address performance bottlenecks
- Streamline authentication processes
- Implement regular policy review cycles
- Develop threat intelligence integration
- Create feedback mechanisms for ongoing refinement
Measuring ZTNA Success: Security Metrics That Matter
Implementing ZTNA is only the beginning of the journey. Measuring the effectiveness of your ZTNA deployment is essential for demonstrating value, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring ongoing alignment with business objectives.Key Performance Indicators for ZTNA
Effective measurement of ZTNA success requires a balanced set of metrics that address security, operational, and business outcomes: 1. Security Effectiveness Metrics:- Reduction in Attack Surface: Measure the decrease in exposed network services and applications
- Policy Violation Incidents: Track unauthorized access attempts and policy violations
- Access Provisioning Time: Measure the time required to grant appropriate access
- Help Desk Tickets: Track the volume of access-related support requests
- Policy Management Efficiency: Measure time spent on access policy administration
- System Availability: Monitor ZTNA component uptime and performance
- Access Success Rate: Track successful vs. failed access attempts
- Authentication Time: Measure the time required for user authentication
- User Satisfaction Scores: Conduct surveys to assess user experience
- Application Performance: Monitor application response times through ZTNA
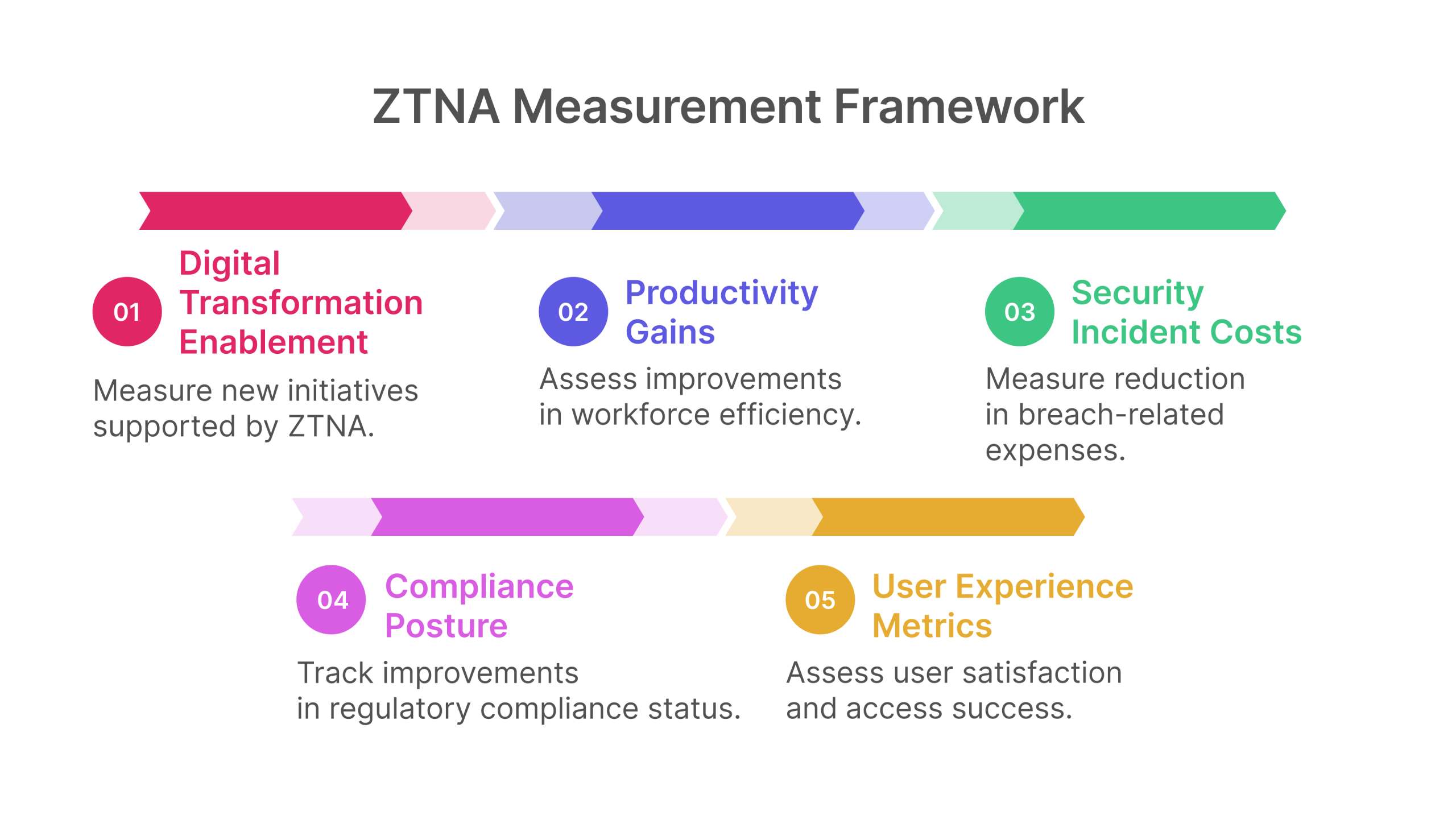
- Compliance Posture: Track improvements in regulatory compliance status
- Security Incident Costs: Measure reduction in breach-related expenses
- Productivity Gains: Assess improvements in workforce efficiency
- Digital Transformation Enablement: Measure new initiatives supported by ZTNA
Establishing a Measurement Framework
To effectively track these metrics, establish a comprehensive measurement framework: 1. Baseline Current State:- Document pre-ZTNA metrics across all categories
- Identify specific areas for improvement
- Set realistic targets for each metric
- Deploy analytics capabilities for security and performance data
- Establish user feedback mechanisms
- Configure automated reporting dashboards
- Conduct monthly operational reviews
- Perform quarterly strategic assessments
- Adjust metrics and targets as the program matures
- Develop executive-level dashboards
- Translate technical metrics into business outcomes
- Demonstrate ROI and value realization
Thinfinity Workspace: Enterprise-Grade ZTNA Without Compromise
At Thinfinity, we understand the complex challenges that CISOs face in today’s dynamic threat landscape. Our Zero Trust Network Access solution, Thinfinity Workspace, is designed to provide comprehensive, scalable, and secure access control that aligns seamlessly with modern security frameworks while addressing the specific needs of enterprise organizations.
How Thinfinity Workspace Addresses Key ZTNA Challenges
Thinfinity Workspace provides unique capabilities that overcome common ZTNA implementation challenges:
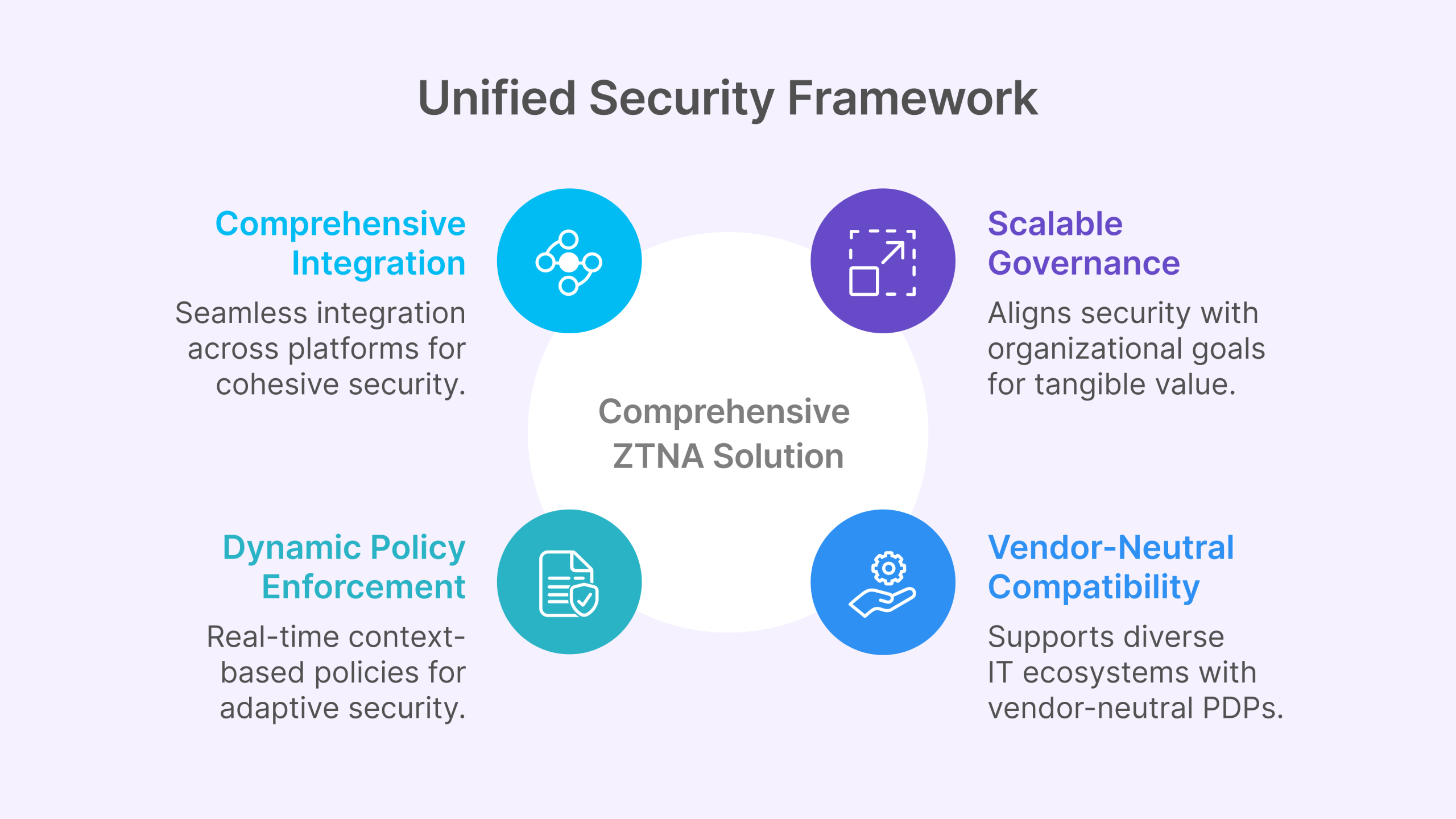
- Comprehensive Integration: Unlike point solutions that create security silos, Thinfinity Workspace ensures smooth integration across various platforms and existing security investments. This unified approach overcomes the challenge of disjointed security products and ensures a cohesive security posture across your entire environment.
- Dynamic Policy Enforcement: While many ZTNA implementations rely on static signals, Thinfinity Workspace facilitates the transition to dynamic access policies. Our solution leverages real-time context-based signals to enhance security, adapting to changing risk levels and user behaviors automatically.
- Scalable Governance: Our governance framework drives measurable business benefits by aligning your security posture with organizational goals. This approach ensures that security investments deliver tangible value beyond technical protection.
- Vendor-Neutral Compatibility: Thinfinity Workspace supports environments with vendor-neutral policy decision points (PDPs), enhancing interoperability and flexibility. This capability is crucial for diverse and complex IT ecosystems that utilize multiple security vendors and technologies.
Thinfinity Workspace Technical Differentiators
What sets Thinfinity Workspace apart from other ZTNA solutions:
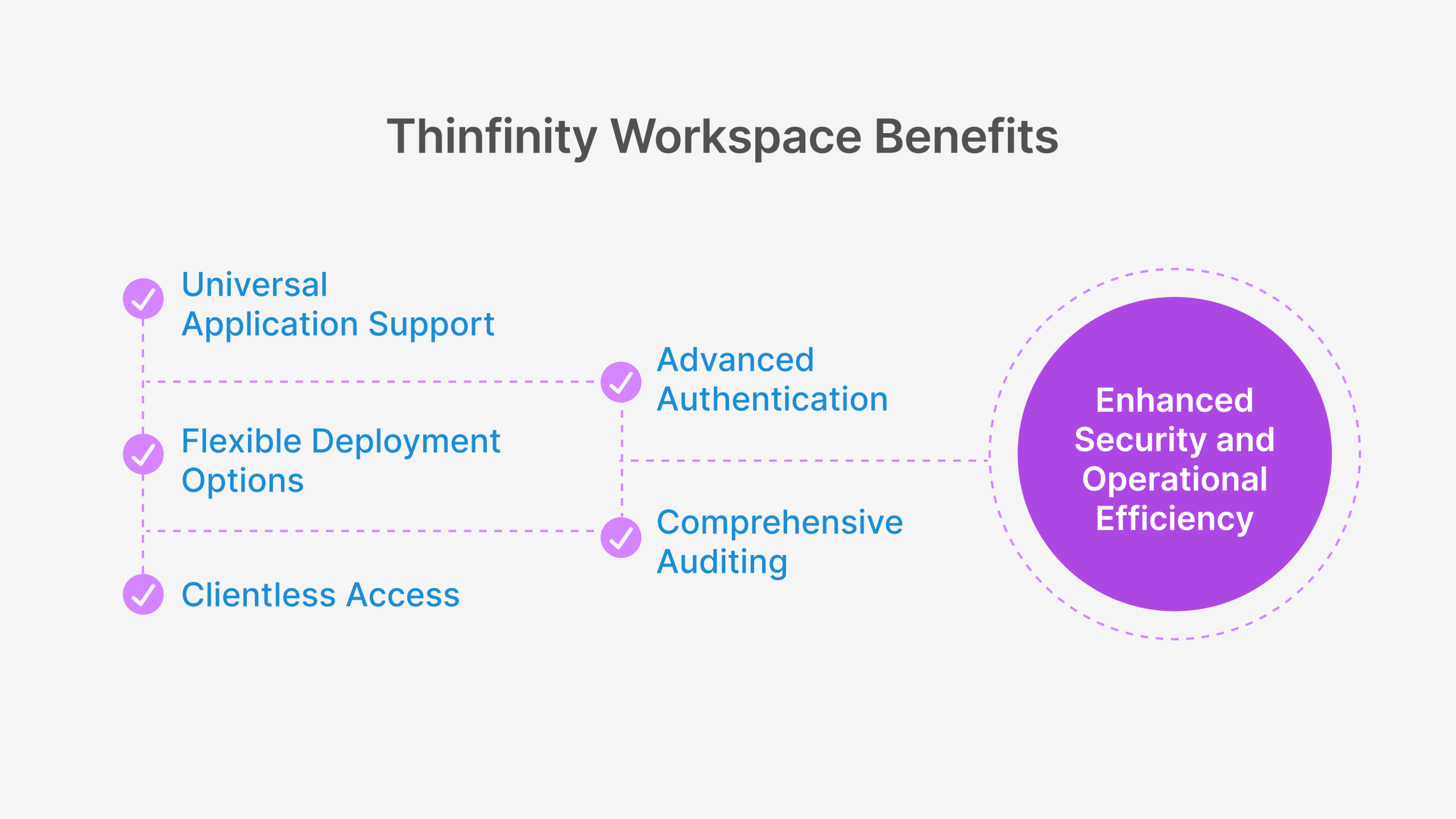
- Universal Application Support: Unlike many ZTNA solutions that only support web applications, Thinfinity Workspace provides secure access to web, legacy, client-server, and custom applications through a single, consistent interface.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Thinfinity Workspace can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid configurations, giving organizations complete control over their security architecture while supporting their cloud migration journey.
- Clientless Access Capabilities: Our HTML5-based clientless access option eliminates the need for endpoint agents in many scenarios, simplifying deployment and supporting BYOD and third-party access use cases without compromising security.
- Advanced Authentication Integration: Thinfinity Workspace seamlessly integrates with existing identity providers and supports multiple authentication methods, including MFA, biometrics, and conditional access policies.
- Comprehensive Auditing and Compliance: Our solution provides detailed session recording, activity logging, and compliance reporting capabilities that simplify regulatory compliance and security governance.
Real-World Results with Thinfinity Workspace
Organizations implementing Thinfinity Workspace as their ZTNA solution have achieved significant security and operational improvements:
70% reduction
reduction in remote access-related security incidents
85% decrease
in VPN maintenance and support costs
40% improvement
in user satisfaction with remote access
60% faster
onboarding for new applications and users
99.9% availability
for critical application access
These results demonstrate how Thinfinity Workspace delivers on the promise of Zero Trust Network Access while providing practical benefits that address the real-world challenges faced by enterprise security teams.
Next Steps: Building Your ZTNA Roadmap
Implementing Zero Trust Network Access represents a pivotal shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. By embracing ZTNA principles and technologies, you can enhance your security posture, reduce risk, and adapt to the ever-evolving threat landscape. Here’s how to begin your journey toward a mature, resilient Zero Trust architecture:
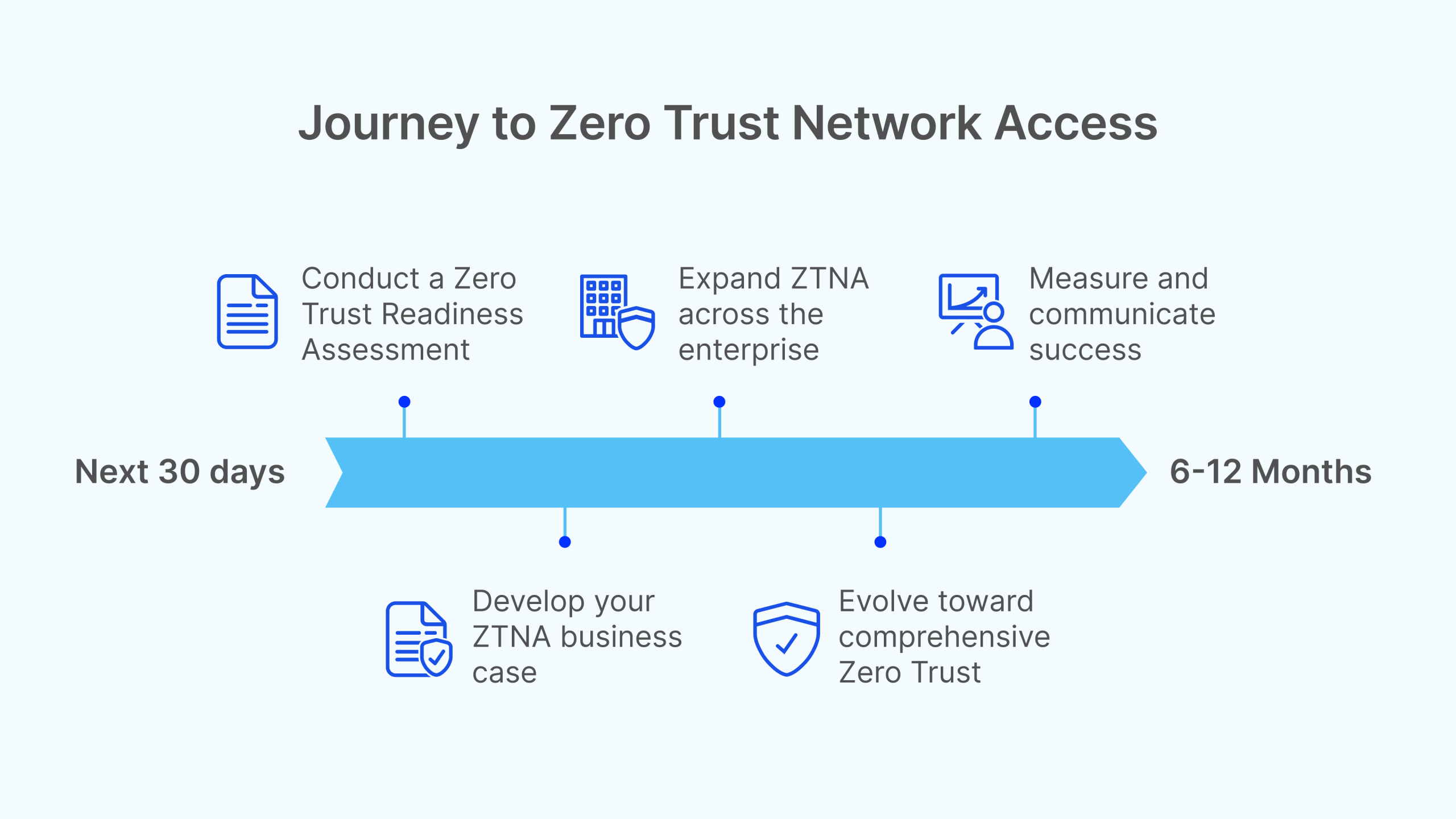
Immediate Actions (Next 30 Days)
1. Conduct a Zero Trust Readiness Assessment:
- Evaluate your current security architecture against Zero Trust principles
- Identify gaps and priority areas for improvement
- Document specific use cases that would benefit most from ZTNA
2. Develop Your ZTNA Business Case:
- Quantify current security risks and operational inefficiencies
- Calculate potential ROI from ZTNA implementation
- Align ZTNA benefits with strategic business initiatives
3. Explore ZTNA Solutions:
- Schedule a personalized demo of Thinfinity Workspace
- Evaluate how our solution addresses your specific requirements
- Discuss implementation approaches with our security experts
Short-Term Plan (60-90 Days)
1. Create Your ZTNA Strategy Document:
- Define scope, objectives, and success criteria
- Develop phased implementation approach
- Establish governance and oversight mechanisms
2. Initiate Pilot Planning:
- Select initial applications and user groups
- Define success metrics and evaluation criteria
- Prepare technical environment for pilot deployment
3. Develop Change Management Strategy:
- Create communication and training plans
- Identify potential resistance points and mitigation strategies
- Establish feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement
Long-Term Vision (6-12 Months)
1. Expand ZTNA Across the Enterprise:
- Implement phased rollout to all user groups and applications
- Integrate ZTNA with broader security ecosystem
- Develop advanced policies and automation capabilities
2. Evolve Toward Comprehensive Zero Trust:
- Extend Zero Trust principles to all security domains
- Implement continuous verification and validation
- Develop advanced threat detection and response capabilities
3. Measure and Communicate Success:
- Track and report on key performance indicators
- Document security improvements and business benefits
- Share success stories and lessons learned
Thinfinity is committed to supporting your journey towards a mature, resilient Zero Trust architecture. Our team of security experts can help you navigate the complexities of ZTNA implementation, ensuring your digital assets are secure against emerging threats while enabling the flexibility and agility your business requires.